
If you’re looking to record your screen or stream online, OBS Studio (formerly Open Broadcaster Software) is a great option. This tool makes it simple to capture screencasts, record your gameplay, stream to Twitch, and much more besides.
However, if you’ve never used it before, OBS Studio might seem a little daunting at first. In this guide, we’ll show you how to set up OBS Studio, what you need to start recording and streaming, and tips for getting the best results.
Download OBS Studio
To get started, you’ll want to download OBS Studio for Windows, macOS, or Linux. We’ll use the Windows version for this tutorial, but it’s similar across all platforms.
OBS Studio is truly free, so you don’t have to pay for any features. It’s also open source software, meaning anyone can look at the code and improve it. This is the case with a popular spin-off: Streamlabs OBS.

Step through the standard installer. Once it completes, OBS Studio will offer to walk you through an auto-configuration wizard. You can do this if you like; we’ll review relevant settings below, though.
How to Use OBS Studio: The User Interface
The main OBS Studio interface allows you to set up everything you need to start streaming or recording. At the bottom of the screen, you’ll see several control elements.
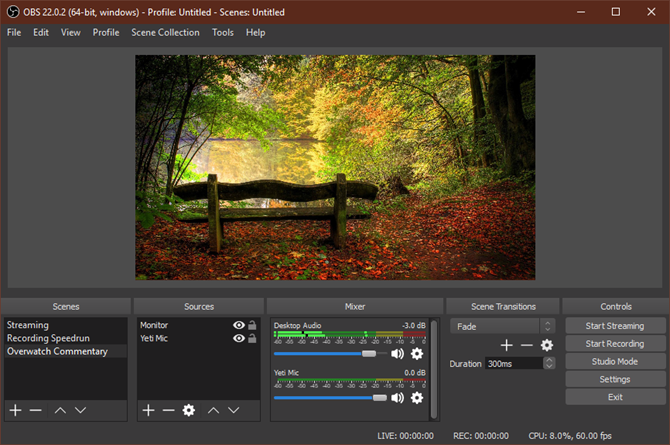
Scenes
A Scene in OBS Studio allows you to collect and arrange certain Source elements in a specific way. You can have multiple scenes and switch between them at will.
This will make a bit more sense as we move on. For now, you can click the Plus button to create a new scene. Call it Default or something similar (you can change it later).
After you’ve added some elements, you can click on them in the preview to adjust as you wish. Click the Eye icon to hide an element, or the Lock to prevent accidental movement.

Sources
Sources are the video and audio inputs that you feed into OBS Studio. Click the Plus button to add a new one, and you’ll see several categories. The most important ones include:
- Audio Input Capture: Record sound from a microphone or similar. (See the best microphones for podcasting if you need one.)
- Audio Output Capture: Capture the sound coming out of your computer, so that your recording/stream includes game or desktop audio.
- Display Capture: Allows you to capture an entire monitor, no matter what’s showing on it.
- Game Capture: Choose a specific game to record.
- Image: Display a static image.
- Video Capture Device: Records footage from a webcam or similar. (We’ve listed the best budget webcams if you don’t have one already.)
- Window Capture: Record a specific program window. This is like Game Capture, but works for any program.
Once you select an option, you can choose Create new or Add Existing. Since you just started, you’ll need to add a new item that you can reuse later. After you click OK, OBS Studio displays options depending on the source you chose.
As an example, click Audio Input Capture. Let’s say you’re going to use a headset microphone to record audio. Enter a descriptive name for the source (like Headset Mic) and click OK. On the resulting screen, pick your headset mic from the Device dropdown and click OK.
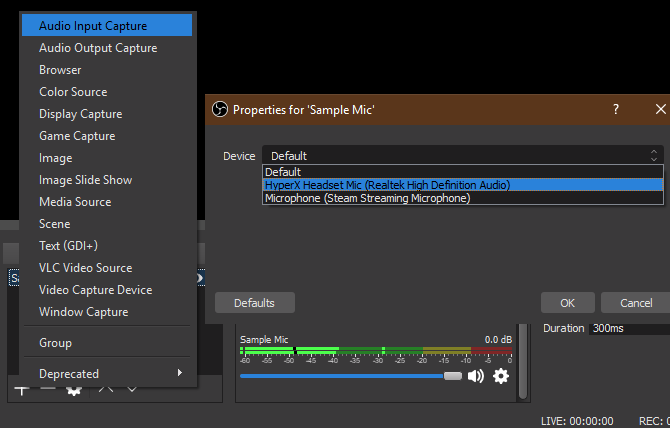
Now, you have that input registered with OBS Studio and can easily add it again in the future. You’ll need to repeat this step to add your webcam, screen capture, and similar.
Audio Mixer
Once you’ve added all of your sources, the Audio Mixer tab lets you adjust the volume balance between them. The bars move in real-time to reflect levels. Drag the slider to adjust the mix, or click the speaker icon to mute one. You’ll find more options by clicking the Gear icon by a source.

You should definitely test these ahead of time, as different sources can have vastly different volume levels. You wouldn’t want to complete a recording only to find out that the game volume overpowers your mic audio.
Scene Transitions
This simple section allows you to choose what happens when you swap between scenes. Choose between Fade and Cut in the dropdown box, or hit Plus to pick another option. You can choose how long the transition lasts using the Duration box.
Controls
Here, the Start Streaming and Start Recording buttons will let you start capturing footage with OBS Studio. You can see the current FPS and CPU usage below.
It also lets you enable Studio Mode for making changes to scenes on the fly, plus access to the many Settings of OBS Studio.
The Best OBS Settings to Use
Before your first recording or stream, you should tweak a few options. Click Settings in the Controls section of the interface to access them.
OBS Studio offers other options than what we explore here, but you shouldn’t need to worry about those until you’re more experienced with recording and streaming.
Video Settings
First, head to the Video tab. Here, check the Base (Canvas) Resolution and Output (Scaled) Resolution) options.
The first should match your screen resolution, while the second lets you choose the resolution of the final video. Leave Output the same as Base for a full-quality recording, or lower it to something like 1280×720 for a lower file size. Leave the Downscale Filter as Lanczos if you’re downscaling.

Lastly, you’ll need to choose the FPS (frames per second) of the recording. For a smooth picture, choose 60. But if you desire a smaller file size or are recording something simple, 30 is suitable.
It’s also a good idea to open the Advanced tab and set Process Priority to High. This will give OBS Studio the most resources so it can create the best recording.
The Best OBS Settings for Recording
Switch to the Output tab to access options related to screen recording—make sure you’re looking in the Recording section, not Streaming.
At the top, you can set the Output Mode to Simple or Advanced. If you want a quick and solid preset, pick Simple and set the following under Recording:
- Recording Quality to Indistinguishable Quality
- Recording format to FLV, or MKV if you prefer
- Encoder to Hardware (AMD) or Hardware (NVENC) if you have a powerful graphics card. Use Software (x264) if not (see below for more details).
- Recording Path to a place of your choosing; this is where your completed OBS video will go.

Under Recording Format, you can choose the video file type to save in (see different video file types, explained for help). The default is FLV, which is fine in most cases. While MP4 is a popular video format, using it is risky because you’ll lose the whole file if OBS Studio can’t finalize it. Thus, a blue screen or power outage would destroy an MP4 recording, but merely cut it off if you’re using FLV.
Below this, you’ll need to choose an Encoder. The default is Software (x264), which uses your CPU. If you have a powerful dedicated graphics card (not integrated graphics), you should change this to Hardware (AMD) or Hardware (NVENC), depending on your card. Doing so will likely provide better results when recording, as it won’t put as much strain on your CPU.
Of course, Advanced gives you more options if you’re comfortable with that. Choose Advanced and swap to the Recording tab below to see them.
What Bitrate Should I Use?
If you switch to Advanced in the Recording panel, many of the additional options relate to the bitrate. This is a vital part of your recording setup. Essentially, a higher bitrate results in better-quality videos with larger file sizes. Setting bitrate too low will result in pixelated video, while setting it too high will generate a massive file.
Thankfully, if you’re using a graphics card encoder, OBS provides a few options to try using the Preset box. Try Recording if you don’t need particularly high quality, and up it to High Quality Recording if that’s not good enough. Indistinguishable Recording and Near Lossless Recording are useful if you need extremely high quality recordings, but be aware that the files will be huge.
If you’re using x264 encoding, you’ll need to set these values manually. There’s no one perfect setting, as the best bitrate depends on your screen size and setup. For 1080p recording at 60FPS, you can start with something like 40,000kbps and adjust from there.
It’s a good idea to try these options to see which provides the best balance of quality and file size. Try recording a minute of typical footage, then use that to estimate how large of a file you’ll end up with.

The Best Streaming Settings in OBS
The Output tab is also home to the Streaming section of options. In Simple mode, you’ll simply need to specify a bitrate, choose between software or hardware encoding, and set the Audio Bitrate.
Twitch recommends certain streaming bitrates depending on quality. 1080p at 60FPS should use a bitrate of at least 6,000, while 720p at 30fps can use something around 3,000. For the audio bitrate, 160 is a good baseline. You can increase this to 192 for better quality, or 320 if you need top-notch audio.
If you want to dive into the Advanced mode, you’ll find options similar to the Streaming tab as discussed above. Users with a graphics card encoder can pick Twitch Streaming from the Preset box as a baseline.
In case you’re using the software encoder, you’ll need to enter the bitrate manually. Use CBR (constant bitrate) for streaming, as VBR (variable bitrate) is inconsistent.

You may wish to lower the bitrate (as well as downscaling the resolution and lowering the FPS if needed) slightly for streaming. A stable, lower-quality stream that everyone can enjoy is better than streaming in maximum quality and having your internet connection struggle to keep up.
Helpful tips for fixing low FPS in games apply here, too. Check out Twitch’s broadcast requirements page for more information.
How to Record Your Screen With OBS Studio
Once you’ve set everything up, to begin screen recording, all you have to do is click Start Recording on the main OBS Studio page. The software will immediately start recording based on the current Scene. You can swap Scenes at any time, so make sure you’ve set them up beforehand.
When you click Stop Recording, OBS Studio will save your file to the directory you specified in Settings. As mentioned earlier, we recommend performing a short test recording first to make sure everything looks and sounds acceptable.
How to Stream Using OBS Studio
To stream with OBS Studio, you’ll first need to connect OBS with your streaming account. Do this by opening Settings and switching to the Stream tab. Under Service, choose your preferred site. You’ll find Twitch, YouTube Gaming, Mixer, and more.

Next, you’ll need to generate a streaming key for the service. Click the Get Stream Key option in OBS to jump right to the appropriate page for your service. To do this with Twitch, for example, head to the Stream Key page in Twitch’s Settings (Settings > Channel and Videos) while logged in. Click Copy and paste this into the Stream Key field in OBS Studio.
Warning: Never give this stream key to anyone or show it on a stream! Anyone with access to this can stream to your account. If you accidentally share it, click Reset to generate a new one.
You’re Now Ready to Record and Stream With OBS Studio
Now you have a basic understanding of how to use OBS Studio. You can customize it a lot more to suit your own personal needs, but this overview is designed to prepare you to record gameplay locally and/or run your first stream.
If you don’t want to bother with OBS, here’s how to record your Windows screen without any extra software.
Read the full article: How to Record Your Screen and Stream With OBS Studio
from MakeUseOf https://ift.tt/2CWJWub
via IFTTT

0 comments: